Wednesday, December 26, 2018
Sunday, December 9, 2018
Wednesday, November 28, 2018
Capacitor & Dielectrics 4
8:50 PM Rohit
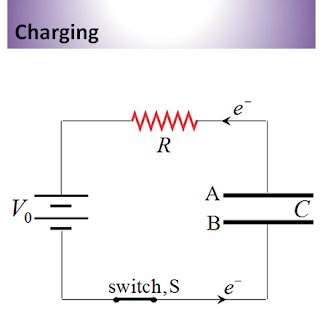
q Electrons will flow out from the negative terminal of the battery, through the resistor R and accumulate on the plate B of the capacitor.
q Then electrons will flow into the positive terminal of the battery, leaving a positive charge on the plate A.
q As charge accumulates on the capacitor, the potential difference across it increases and the current is reduced until eventually the maximum voltage across the capacitor equals the voltage supplied by the battery, Vo.
q At this time, no further current flows (I = 0) through the resistor R and the charge Q on the capacitor thus increases gradually and reaches a maximum value Qo
V0 = VR + VC, VR = IR, VC = Q/C
At t = 0, V0 = VR, VC = 0
During charging, V0 = IR + Q/C, I in resistor decreasing, Q in capacitor increasing
As t ® ¥, V0 = VC, VR = 0
•Initially, the potential difference (voltage) across the capacitor is maximum, V0 and then a maximum current I0 flows through the resistor R.
•When part of the positive charges on plate A is neutralized by the electrons, the voltage across the capacitor is reduced.
•The process continues until the current through the resistor is zero.
•At this moment, all the charges at plate A is fully neutralized and the voltage across the capacitor becomes zero.
V0 = VR + VC, VR = IR, VC = Q/C
At t = 0, V0 = VC, VR = 0
During discharging, V0 = IR + Q/C, I in resistor decreasing, Q in capacitor decreasing
As t ® ¥, V0 = VR, VC = 0
Capacitor & Dielectrics 3
7:49 PM Rohit
Consider a parallel-plate capacitor
· Initially the plates are separated by a vacuum and connected to a battery, giving the charge on the plates +Q and –Q
· The battery is now removed and the charge on the plates remains constant
· The electric field between the plates is uniform and has a magnitude of E0
· Meanwhile the separation between plates is d
|
· When a dielectric is placed in the electric field between the plates, the molecules of the dielectric tend to become oriented with their positive ends pointing toward the negatively charged plate and vice versa
· The result is a buildup of positive charge on one surface of the dielectric and of negative charge on the other
|
· The number of field lines within the dielectric is reduced thus the applied electric field E0 is partially canceled
· The new electric field, E is electric field between the plates is uniform and has a magnitude of E0
· The new electric field strength (E < E0) is less, then the potential difference, V across the plates is less
V = Ed
· Since V is smaller while Q remains the same the capacitance
C = Q/V
is increased by the dielectric
| |
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)