Capacitor & Dielectrics 4
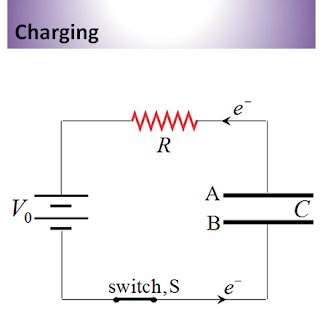
q Electrons will flow out from the negative terminal of the battery, through the resistor R and accumulate on the plate B of the capacitor.
q Then electrons will flow into the positive terminal of the battery, leaving a positive charge on the plate A.
q As charge accumulates on the capacitor, the potential difference across it increases and the current is reduced until eventually the maximum voltage across the capacitor equals the voltage supplied by the battery, Vo.
q At this time, no further current flows (I = 0) through the resistor R and the charge Q on the capacitor thus increases gradually and reaches a maximum value Qo
V0 = VR + VC, VR = IR, VC = Q/C
At t = 0, V0 = VR, VC = 0
During charging, V0 = IR + Q/C, I in resistor decreasing, Q in capacitor increasing
As t ® ¥, V0 = VC, VR = 0
•Initially, the potential difference (voltage) across the capacitor is maximum, V0 and then a maximum current I0 flows through the resistor R.
•When part of the positive charges on plate A is neutralized by the electrons, the voltage across the capacitor is reduced.
•The process continues until the current through the resistor is zero.
•At this moment, all the charges at plate A is fully neutralized and the voltage across the capacitor becomes zero.
V0 = VR + VC, VR = IR, VC = Q/C
At t = 0, V0 = VC, VR = 0
During discharging, V0 = IR + Q/C, I in resistor decreasing, Q in capacitor decreasing
As t ® ¥, V0 = VR, VC = 0